Climate in Japan
The mainland of Japan belongs to Temperate Zone.
The northernmost Hokkaido Island is in a subarctic zone, and Okinawa islands in the southwest part are in the subtropics.
Roughly speaking, cool and dry air mass on the Continent of Asia from the northwest and hot and wet air mass on the ocean from the south meet around Japan.
Each of them becomes stronger or weaker by season and moves around Japan.
In addition, there are relatively high mountains along the long mainland.
It is like a wall for the air masses, so the rising air currents cause rain or snow.
That creates the typical climate of Japan.
As you can see the map of Japan, the east half of the mainland is long from north to south and the west half is long from east to west.
So, in Tohoku and Hokkaido regions, the farther north you go, the lower the temperature becomes.
On the other hand, because the west part from Kanto region include Tokyo, Kyoto, Fukuoka is located around the same degree of latitude, the temparature is about the same in the area.
Spring (from March to May)

Ume blossoms in Dazaifu-tenmangu Shrine in Fukuoka Prefecture
During winter, the air mass from very cold Continent covers Japan.
From around late February, it becomes weak little by little.
In March, the sunshine becomes a little warm.
In this period, the blossoms of "ume" (Japanese apricot) are in full bloom in mainland.
This is the scene of early spring in Japan.
Because the air mass of cold Continent becomes weak, low pressures often pass around Japan from west to east. When it passes, rain falls.
After rain, the tempearture falls a little, but it is getting warmer and warmer.
This is the climate of spring in Japan.

Cherry blossoms in Arashiyama in Kyoto
From around the end of March, "sakura" (cherry blossoms) begins to bloom in the south part of mainland.
It becomes in full blooming in the early April, and the scene gradually moves northward.
This is the start of mid-spring.
From around late April to May, the temperature continue to rise little by little.
In this season, we feel very comfortable.
Many days are nice weather, and the season move to early summer.
But, in Hokkaido, this season is about a month later than the above area.
In contrast, Okinawa area is about a month earlier.
Tsuyu (from early June to mid-July)

Hydrangea in a Buddhist temple in tsuyu season
Dry air mass of the continent has continued to give comfortable climate to Japan until around May.
But hot and wet air mass on the Pacific Ocean to the south of Japan becomes stronger gradually in June.
They struggle with each other, therefore, a stationary front is formed around Japan from west to east.
Around the stationary front, rainy or cloudy weather continues every day.
In Japan, this rainy season is called as "tsuyu" or "baiu", and the stationary front is also called "baiu front".
When the condition of tsuyu is formed clearly, Japan Meteorological Agency announces the start of tsuyu ("Tsuyu-iri" in Japanese).
The temperature in this season becomes over 30 °C and humidity is high.
This season continues over a month until mid-July.
In Okinawa islands area, this season is about a month earlier than the mainland.
Hokkaido is far from the stationary front, so tsuyu doesn't go to Hokkaido.
Rain in the last stage of tsuyu falls heavily, and sometimes cause floods.
In mid-July, the hot and wet air mass increases its strength and pushes the the stationary front up to the north gradually.
In the southern areas of the stationary front, rain clouds disappear.
And strong sunshine and hot air cover the area.
On the day, Japan Meteorological Agency announces the end of tsuyu ("Tsuyu-ake" in Japanese) in the area.
It is also the start of mid-summer.
The speed to go up north is fast, so the stationary front disappears from whole Japan by the end of July.
Summer (from mid-July to August)

Young people in an event place in midsummer
After tsuyu, the mainland of Japan becomes hot summer.
Basically, wide area of Japan is covered with hot high pressure on the Pacific Ocean.
It sends hot and moist air to Japan.
In many areas, the temperature is over 30 °C. And the humid is high.
Recently, it is not unusual that the temperature reaches between 35 and 40 °C.
In addition, the temperature is over 25 °C even in the night.
Such night is called as "tropical night" in Japanese.
So, it is often said that the summer of Japan is hotter than Southeast Asia.
Sometimes, towering thundercloud appears locally in the afternoon, and there is a sudden shower.

A cicada on a tree trunk
When Europeans and Americans visit Japan in the mid-summer, they are surprised at the sound of cicada, which is a kind of insects and sings like a buzzer on a tree trunk.
A lot of cicada are on many trees even in the center of the city, so you hear the loud sound everywhere.
You may feel it as a noise, but Japanese people feel it a common feature in the summer time.
(Cicada is a harmless insect.
It lives in the ground as a larva for some years, then becomes an adult insect on the ground.
But the lifetime as an adult insect is within a month.)
In this season, typhoons are often born on the Pacific Ocean.
A few of them come to Japan in this season every year.
Of course, the average temperature in Hokkaido is 4 to 5 °C lower than the mainland.
Okinawa island is in the subtropics, but the temperature in midsummer is rather a little lower than the mainland.
Autumn (from September to November)

The street of colored gingko trees in Tokyo
In early September, the sunshine is still strong.
But, the air mass of the Continent is becoming strong again and it sometimes sends dry and cool air to Japan.
The air mass of the south ocean begins to withdraw, because the lengths of day and night will be nearly equal and the power of the sun is weakning.
Both air masses struggle with each other again, but the period is not so long as tsuyu.
Then, in October, cool and comfortable season comes in the mainland.
Every year, about three to five typhoons pass through Japan.
Amongst that, September is the most dangerous month.
In the past, some typhoons in September caused great damage in Japan.
If you stay in Japan in September, you should check the weather forecast every day.
The climate in October and November is like April and May.
Rather the air is drier than the season of spring.
In autumn, low pressures sometimes pass on Japan from west to east.
Cold rain falls at that time, but it is generally fine on the other days.
The days are getting shorter and shadows become longer.
And, the leaves began to color.
By the effects of global warming, autumn leaves are seen from late November to early December in the mainland.
In Hokkaido and the north part of Tohoku region, the season of autumn proceeds to winter about a month earlier than the mainland.
Winter (from December to February)

A rare snowy day in Tokyo
December may be the last period of late autumn.
In early December, we can see the last autumn leaves and the temperature is not so low in the mainland.
Surely, the cold air mass of the Continent is covering Japan.
And the temperature is falling gradually.
But, we living in the south part of mainland feel real winter around Christmas.
The date of the first snow is in early November in Hokkaido, in late November in Tohoku region, and in early December in the other snowy area.
So, main ski resorts are opened after mid-December.
Between Janauary and early February, very cold air mass from the Continent covers the mainland of Japan.
The air mass is very strong. So, the same weather continues every day in winter.
But, in late Febrauy, the weather begins to change.
Low pressure sometimes passes around Japan, and the air of spring are pulled from south.
Then, the cold season becomes the warm season gradually.
Snow-covered area in Japan

Shirakawago in winter
Recently, the visitors to Japan for "snow" are increasing.
For example, Australians visit Hokkaido for skiing on nice snow.
The visitors from Southeast Asia visit any snowy area to see snow for the first time in their life.
But, snow falls much only in the limited area.
It depends on the geographical feature of Japan and the climate of winter in the east Asia.
In winter, the temperature of the air in Siberia drops to 40-50 degrees below zero.
The area becomes a high-pressure zone, and very cold seasonal wind flows out to the environment.
The wind crosses the Sea of Japan.
In the Sea of Japan, warm current is flowing along Honshu Island.
Therefore, the air absorbs much water-vapor because of temperature difference.
The very cold and wet air reaches Honshu islands, but steep mountains stand up there.
The air scrambles up the mountains and makes thick clouds extensively.
Because the clouds contain considerable moisture and the temperature is low, much snow falls there.
As the wind from Siberia comes one after another, the snowy weather continues in the area facing the Sea of Japan almost every day during winter.
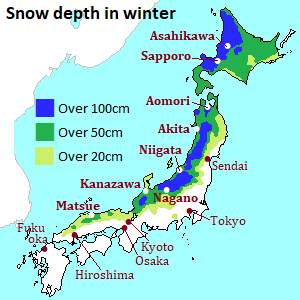
Probably, Japan is a country with one of the world’s heaviest snowfall area.
Some cities get over 1 meter of snow and there is a town where gets over 4 meters every year.
Getting back to the point, the wind which has lost moisture crosses over the mountains.
The dry wind blows on the areas of the Pacific side.
In the area, there are main big cities such as Tokyo, Nagoya, Kyoto, Osaka, Fukuoka, Sendai, etc.
The distance between the mountain and the coastline is not so long.
Because the air has no time to absorb water-vapor, no or little cloud appears.
Therefore, fine weather continues almost every day on the Pacific Ocean side.
This area has snow only several times a year, and is covered with snow only a few times.
It is rare that snow continues for over 2 days, and the weather usually turns fine the next day.
Then, the covering of snow melts and disappears within a few days.
If you visit Tokyo, Kyoto and encounter the snow scene there, you may be lucky.
But, the big cities such as Tokyo are unaccustomed to snow.
Even several centimeters of snow causes a traffic disturbance, and many people fall on an icy sidewalk.
When you stay there in such days, you may be forced to change your plan.
As above, the climate in winter differs according to area.
Please check the map of snow-covered area in winter.


